

O but they have very different chemical and physical properties. For example, ethanol (See Figure 1.) and dimethyl ether (See Figure 2.) are two isomers with the molecular formula C When the same atoms are arranged in different ways, they produce new substances called isomers. The same atoms can be rearranged in various ways to form a number of molecules that each have distinct physical and chemical properties. Furthermore, the specific arrangements and interconnections between atoms within a molecule determine its properties. ), a toxic gas, and sodium (Na), a highly reactive metal. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl), otherwise known as table salt, is formed from the combination of chlorine (Cl Two or more atoms can combine in ways that form compounds with very different properties from those of its individual atoms. The periodic table organizes the 118 known elements by increasing atomic number and bears its name because the elements in the vertical columns share many physical and chemical properties-which is to say that the properties repeat periodically.Ītoms combine to form more complex units, called molecules. Elements cannot be broken down by normal chemical means, so they are considered the most basic building blocks for creating compounds, or molecules. Elements are composed of all atoms with the same atomic number (number of protons) and are the smallest units that still retain their characteristic chemical properties. Forensic scientists measure both types of properties, but intrinsic properties are most useful in terms of identifying substances at a crime scene.Īll matter can be broken down into atoms, which are the simplest units of chemical importance. For example, mass, volume, and heat content are all considered extrinsic properties. Extrinsic properties do depend on the size of a sample.
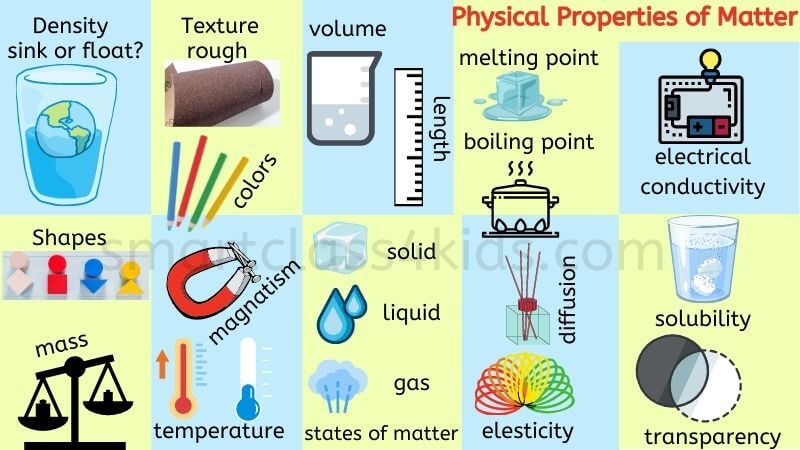
Melting point, boiling point, density, odor, and color are all considered intrinsic properties. Intrinsic properties are not dependent upon how much material is present. Some properties depend upon how much material is present in a sample, while other properties do not. Chemical properties include: flammability, pH, and reactivity with water. Physical properties include: magnetic attraction, density, boiling point, freezing point, melting point, solubility, color, and odor.

Physical properties are dependent upon the chemical structures and features of substances, i.e., how their molecules and/or atoms are arranged in space and how much energy is available to them. Physical properties are those that can be measured without having to change a material’s chemical identity. Chemical properties are those that can only be measured by attempting to change the chemical identity of a material through a chemical reaction. Physical and chemical properties are both used to describe matter. Everything that has mass and volume is made of matter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
